Dna Slot Blot Protocol
Blotting is primarily used in molecular biology. It is used to identify proteins and nucleic acids for diagnostic purpose. Specifically, blotting is used for identifying biomolecules like DNA, mRNA, and protein during gene expression.


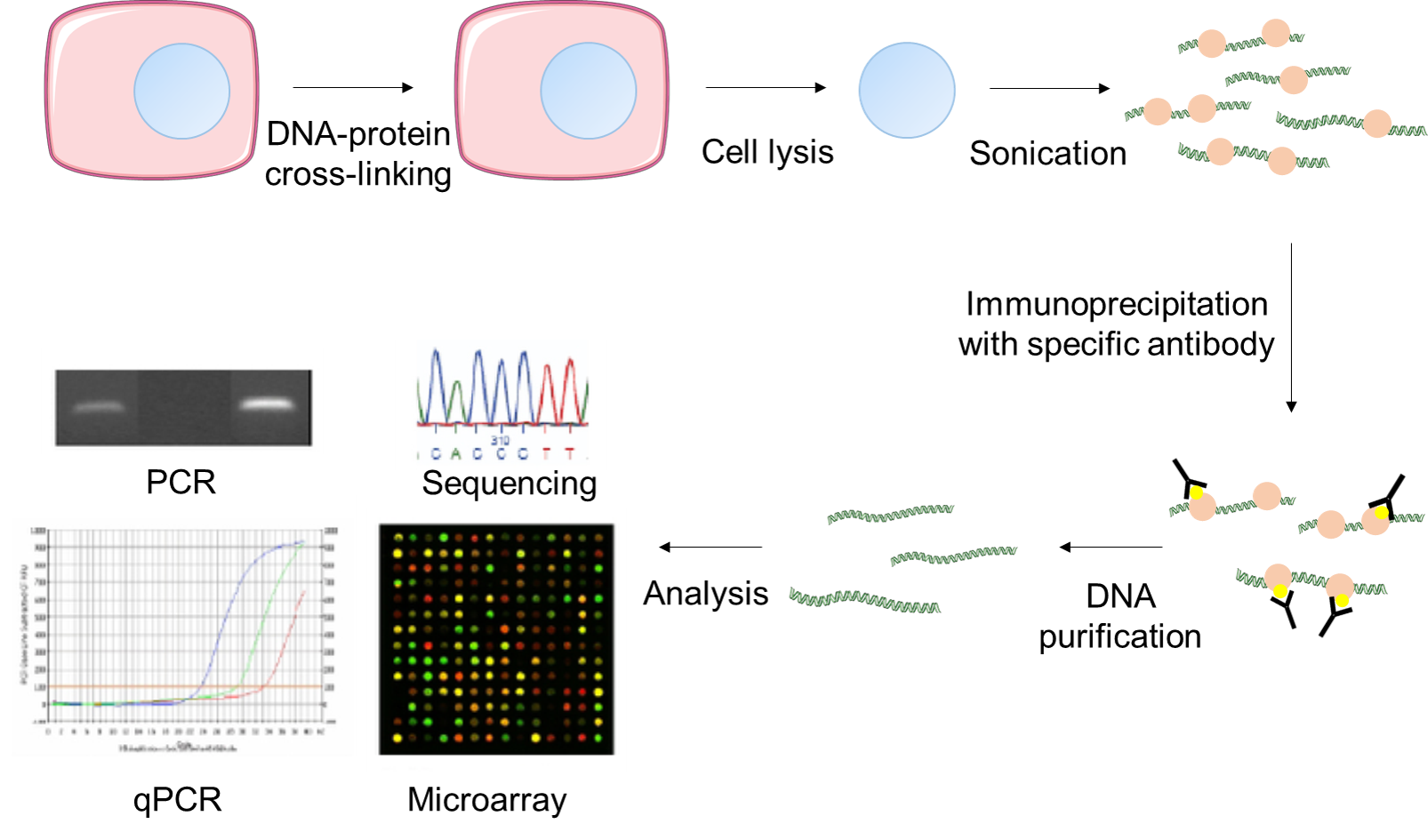
- Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. Dot and slot blots differ only in the geometry of the blot, a series of spots giving a hybridization pattern that is amenable to.
- Load the samples into the wells of the slot blot or dot blot apparatus and transfer the DNA to two nylon membranes–one for each strand-specific probe. After the samples have transferred to the membrane, rinse the sides of each well with 500 µl of 10x SSC.
- Abstract Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations.
- (1998) Quantification of DNA By Slot-Blot Analysis. In: Lincoln P.J., Thomson J. (eds) Forensic DNA Profiling Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 98.
Slot blot quantitation can help determine whether the DNA is human or non-human. DNA quantitation must be accomplished on all samples by yield gel and/or slot blot before amplification. Slot blot is required for all unknown samples. It is not required for standard samples. The decision to use slot blot on standard samples is left to the.
DNA and RNA molecules need to undergo biochemistry analysis and they are separated using the blotting method.
Picture : A helpful mnemonic for students to remember the relation between various blotting methods and its uses
Blotting is done by enabling the mixture of molecule pass through a gel that separates the molecules based on their molecular size. The molecules being tested are hard-pressed against a membrane which will then transfer the molecule from the gel onto the suitable membrane through capillary action.
One of the commonly used blotting procedures is Southern blotting. This procedure was introduced in 1975 by Edwin Southern; thus, where the name was taken. What is Southern blotting? It is a blotting method used to detect a particular sequence of DNA in a DNA sample. There are other subtypes such as Northern blotting, Western blotting, South-Western blotting, and Eastern blotting. (1, 2, 3, and 4)
Image 1: The Southern blot procedure as shown in the image above.
Picture Source: thescienceinfo.com
What does Southern blotting reveal?
A southern blot analysis reveals the following:
- Identity of the DNA
- Size of the DNA
- Abundance of the DNA (4, 5)
The Southern blotting method is a classic technique that separates DNA fragments according to their size through electrophoresis. They will be transferred to a membrane, hybridize, washed, and lastly, detecting the labeled DNA band.
How much DNA is needed for Southern blotting?
The amount of DNA needed varies depending on the size and specific activity of the probe.
What is the principle of Southern blotting?
Southern blotting is a restriction fragment length polymorphism. It is a hybridization method for identifying the size of DNA from a mixture of other similar molecules. Basically, Southern blotting separates DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are identified using a labeled probe hybridization. (5, 6, and 7)
What are the steps in Southern blotting?
Dna Slot Blot Protocol Igg
There are a series of steps that need to be strictly followed when performing Southern blotting. They are the following:
Image 2: The first and second step of southern blot method.
Picture Source: slideplayer.com
#1 – Restriction Digest
A restriction enzyme is used to fragmentize the DNA. The DNA is cut at a specific site generating a fragment. The DNA fragments obtained by restriction digest are amplified by PCR. (7, 8)
#2 – Gel electrophoresis
Once the DNA fragments are obtained, the next step is separating the DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis.
Image 3: The denaturing of DNA.
Picture Source: slidesharecdn.com
#3 – Denaturation
An SDS gel is needed in this step. Once electrophoresis is done, the SDS gel is soaked in either acid like HCl or alkali like NaOH. The purpose is to denature the fragments of double-stranded DNA. After denaturation, the strands of DNA will separate. (8, 9)
#4 – Blotting
This is where the actual bloating takes place. The DNA’s separated strands are transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane through the process of blotting.
Blotting process is done so as to determine the nature of DNA
#5 – Baking and Blocking
.jpg)
The DNA is based on autoclave and fix in the membrane. Casein or Bovine serum albumin is used to treat the membrane. What these chemicals do is they saturate the membrane’s binding site.
#6 – Hybridization with labeled probes
A labeled probe is used to treat the membrane-bound DNA. It has complementary sequences to the gene being studied on. The probe will bind with the complementary DNA on the membrane. (3, 7, and 10)
Dna Slot Blot Protocol Assay
#7 – Visualization by Autoradiogram
Dna Slot Blot Protocol Definition
An autoradiogram is used to visualize the membrane bound DNA that is labeled with a probe. Autoradiogram visualization provides a pattern of bands.
Why is Southern blotting important?
Image 5: A southern blot is one of the procedures used in paternity testing.
Picture Source: slideplayer.com
Southern blotting is important as it is useful in the various field of interest such as:
- It is used in detecting the DNA in a given sample such as DNA fingerprinting in forensics.
- It is useful in isolating and identifying the gene of interest.
- In forensics, southern blotting is one of the commonly used procedures, especially in:
- Criminal identification
- Victim identification
- It is used for paternity testing.
- It helps identify gene rearrangement or mutation in a particular sequence of DNA/gene mapping.
- It is used to diagnose a particular disease caused by genetic defects.
- It is helpful in identifying infectious agents.
- It helps in restricting fragment length polymorphism.
- It has the ability to identify a single gene in a pool of DNA fragments.
- It helps detect cancer and genetic diseases like sickle cell mutation and monoclonal leukemia. (1, 3, 5, and 8)
How is Southern blotting used in forensics?
Forensic laboratories used southern blotting method to detect the smallest quantity of DNA, especially in the case of rape, thieves, or identification of parenthood. (7, 8)
Image 6: Southern blotting is a procedure used in a forensic setting such as in the case of rape and other types of crimes that may require identification of DNA samples.
Picture Source: newyorker.com
Summary
Southern blot is a method commonly used in molecular biology. It has been a widely used technique for over three decades. Through southern blot, researchers can thoroughly understand the fundamentals of molecular biology. The primary purpose of southern blot is to detect a sequence of DNA in a given DNA sample.
However, the southern blotting method can be quite expensive and extremely technical in nature. Sample-wise, it needs a large quantity of DNA, which is not always favorable in some settings.
With the advancement in the field of science and medicine, new DNA testing methods were developed such as PCR. It is better than southern blotting because the procedure involved is very straightforward. It is easy, fast, reliable, and only requires a small volume of DNA. (2, 4, 6, and 9)
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Southern_blot
- https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/southern-blotting-principle-procedure-application/
- https://www.thermofisher.com/ph/en/home/life-science/dna-rna-purification-analysis/nucleic-acid-gel-electrophoresis/southern-blotting.html
- https://askabiologist.asu.edu/southern-blotting
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/southern-blot
- https://www.mybiosource.com/learn/southern-blotting/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18432697
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-is-Southern-Blotting.aspx
- https://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/Gr12-18.html
- https://www.nature.com/wls/definition/southern-blot-289
Related Posts:
Probably the most commonly used method in forensic labs today for genomic DNA quantitation is the so-called 'slot blot' procedure. This test is specific for human and other primate DNA due to a 40 base pair (bp) probe that is complementary to a primate-specific alpha satellite DNA sequence D17Z1 located on chromosome 17 (Waye et al. 1989, Walsh et al. 1992). The slot blot assay was first described with radioactive probes (Waye et al. 1989) but has since been modified and commercialized with chemiluminescent or colorimetric detection formats (Walsh et al. 1992).
Slot blots involve the capture of genomic DNA on a nylon membrane followed by addition of a human-specific probe. Chemiluminescent or colorimetric signal intensities are compared between a set of standards and the samples (Figure 3.3). Slot blot quantitation is a relative measurement involving the comparison of unknown samples to a set of standards that are prepared usually via a serial dilution from a DNA sample of known concentration. While comparison of the
Figure 3.3

Illustration of a human DNA quantitation result with the slot blot procedure. A serial dilution of a human DNA standard is run on either side of the slot blot membrane for comparison purposes. The quantity of each of the unknown samples is estimated by visual comparison to the calibration standards. For example, the sample indicated by the arrow is closest in appearance to the 2.5 ng standard.
Calibration standards | ,-A-N | Calibration standards | ||
20 ng | m | -2.5 ng * | - | 0.63 ng |
10 ng | — | — | 1.25 ng | |
5 ng | — | — | 2.5 ng | |
2.5 ng | — | 5 ng | ||
1.25 ng | - | 10 ng | ||
0.63 ng | - | ■ | 20 ng |
DNA standards and unknown samples on the slot blot membrane is often performed visually and therefore influenced by subjectivity of the analyst, digital capture and quantification of slot blot images has been demonstrated with a charged-coupled device (CCD) camera imaging system (Budowle et al. 2001).
Typically about 30 samples are tested on a slot blot membrane with 6-8 standard samples run on each side of the membrane for comparison purposes. For example, the standards might be a serial dilution of human DNA starting with 20 ng, 10 ng, 5ng, 2.5 ng, etc. Typically only 5 L of DNA extract is consumed for this quantification test.
The assay takes several hours to perform but is fairly sensitive as it can detect both single-stranded and double-stranded DNA down to levels of approximately 150 pg or about 50 copies of human genomic DNA. A 150pg DNA standard can be detected after only a 15 minutes exposure to X-ray film (Walsh et al. 1992). With chemiluminescent detection, the sensitivity can be extended below 150 pg by performing longer exposures to the X-ray film and blotting additional low dilution DNA standards on the membrane. Levels of 10-20 pg have been reported with a three-hour exposure (Walsh et al. 1992). Even when no results are seen with this hybridization assay, some forensic scientists still go forward with DNA testing and often obtain a successful STR profile. Thus, the slot blot assay is not as sensitive as would be preferred.
As of early 2004, the slot blot assay is available as a commercial product from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA) called the QuantiBlot Human DNA Quantitation Kit. This kit uses a DNA probe from chromosome 17 and is thus useful for determining the level of human DNA present in a sample. It is important to note though that this assay, as with most 'human-specific' tests, works on primates such as chimpanzees and gorillas due to similarities in human and other primate DNA sequences.
Was this article helpful?